Today’s economy is experiencing profound transformation driven by the digital revolution and the green transition. The two phenomena have been termed the “twin transition” (EC, 2020). Like every other twin, they can advance each other and can also clash. While one aims to adopt the latest technological advancements to the workplace by reshaping industries and work processes, the other advocates for the promotion of sustainability and reduction of carbon emissions as a way to address environmental issues.
As advancements in digitization get better by the day, there is an ongoing fear that it will result in massive job loss. The world economic forum estimates about 85 million jobs will be lost due to the digital automation of work processes by 2025. While this has generated a lot of skepticism among workers, especially the aged ones, the process is expected to create additional 95 million new jobs in the same period.
Apart from the opportunities that come with the digital and green transition which includes job creation, investments in innovation and the green economy, expansion of digital jobs, etc, it also poses several challenges including job loss, skills mismatch and labor shortages, technological divide, and access, inequality and social exclusion, to name a few.
As the digital and green transitions drive changes in the labor market, which includes the creation of new jobs and upgrades to the old ones, workers and organizations must adjust accordingly by investing in training, re-skilling and upskilling, change in attitude to work, to name a few in other to actualize the potentials of these transitions and to avert the issues of unemployment.
Nonetheless, since young people have good knowledge of digital technology, it is expected that these transitions will benefit them the most. For example, every young person (16 – 24 years old) in the EU has basic or above basic digital skills. Countries like Iceland, Norway Switzerland, Croatia, Netherlands Estonia, Greece, Czech Republic, and Lithuania have a higher rate of digital skill (above 90%).
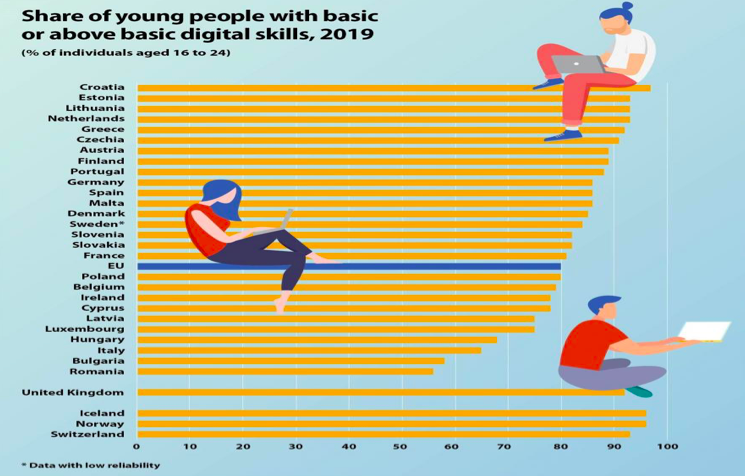
Source: Eurostat
For digital and green transitions to be successful, it is not enough to have basic digital skills. Investment in training, devoting time, and commitment are required to learn and gain new skills. This will ensure the younger generation is not left out of the digital revolution and green transition. This will also reduce unemployment and social inequality challenges that may arise due to the transformation.
Considering the digital revolution and green transitions, one question that comes to mind is the digital skills needed to penetrate the market. While hard skills are sought after in the market, employers are also looking for workers with more soft skills to complement the hard skills possessed. According to the Future of Jobs report conducted by the world economic forum, employers are looking to onboard workers with cognitive skills (analytical and creative thinking), Self-efficacy (resilience, flexibility, agility, curiosity, life-long learning, motivation, and self-awareness), management skills (Quality control), technological skills (technological literacy), positive work attitude (empathy, active listening, leadership, and social influence). In addition to the soft skills mentioned, the following digital skills are needed in other to remain relevant and employed in the wave of the digital revolution.
- Digital and social media marketing
Marketing teams use data gathered from digital channels for social or digital marketing to evaluate the efficacy of their campaigns and develop new strategies. When creating such marketing strategies and campaigns, having skills like optimizing keywords, marketing on social media, and improving user experience and engagement can be helpful.
- Search engine optimization
As someone who aspires to work in the marketing and social media campaign, having an SEO skill will come in handy, especially at the age when companies and organizations are seeking to showcase their products and services to more people thereby reaching the target audience. SEO professionals are responsible for using tools necessary to increase the visibility of a product or service belonging to an organization or a company.
- Cybersecurity
As the world advances toward digitization and lives begin to revolve around computers and the internet, investments in digital security also become paramount, especially for organizations and businesses. This necessitates skillful professionals to make the digital world safe from cyber-attacks and hazards.
- Artificial intelligence and Machine learning
Recent investment in digital automation have been on the rise and more companies are investing in artificial intelligence to drive their digitization and optimization processes. For instance, jobs like customer service, customer representatives and graphic designing to mention a few are being performed by AI bots. Therefore, professions with AI skills such as automation engineer, process optimization engineer, etc are sought after by employers in the field.
- Web development, web design and software development
Organizations highly demand skills in mobile and web application design and development. Companies are moving to utilize digital platforms for sales and to reach more customers. Recent events such as Covid-19 saw more demand for digital presence for businesses and more IT personnel. Almost every sector of the economy, from accommodation to construction saw an increase in online presence since the beginning of the pandemic across Europe in 2020. This necessitates IT professionals to create, design and maintain their online activities.
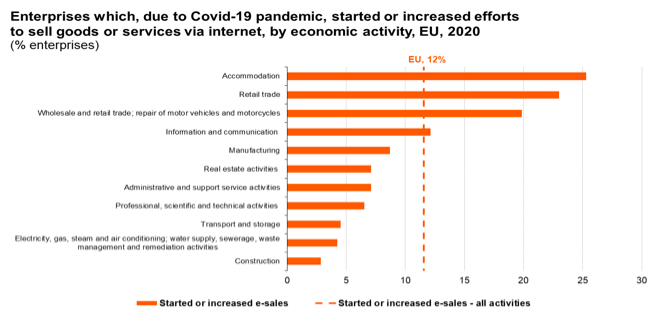
Source: Eurostat
In conclusion, In the wake of the digital era, constant training and active learning play a vital role in equipping young people with the necessary digital skills to thrive in the job market. By actively engaging in training opportunities, young individuals can stay abreast of technological advancements, enhance their employability, and contribute meaningfully to the digital economy.
References:
- Joint Research Centre (2022) europa.eu- The twin green & digital transition.
- Top 5 Digital Skills You’ll Need in 2021 (and Possibly in 2022 Too) (2022) workforce Singapore.
- Indeed job portal. https://in.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/digital-skills
- World economic forum (2023). Future of job report 2023. https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_2023.pdf


